

The main source of antimony in urban air is the combustion of fossil fuels in incinerators, power plants and motor cars. The maximum level of antimony allowed in drinking water in European countries is 0.006 ppm. The defined occupational exposure limit is only 0.5 mg of antimony per m3 of air for 1 working day of 8 hour duration. High levels of antimony in inhaled air for long periods can irritate the lungs and eyes and cause heart, respiratory and stomach problems. Most of the antimony in the air goes to the ground where it is deposited and binds tightly to particles made of aluminum, manganese or iron.
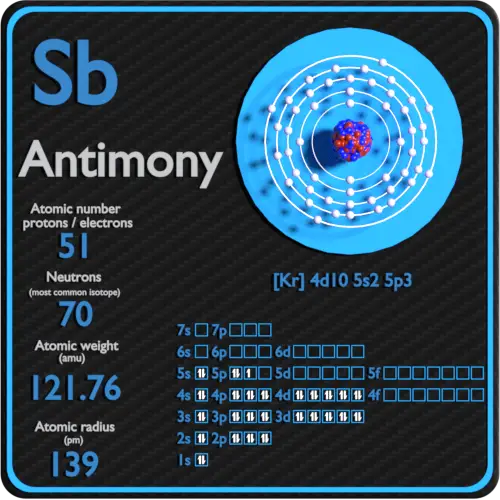
It remains attached to the air in small particles for several days. Antimony and its configuration in the environmentĪntimony is released into the environment from industrial and natural sources. It crystallizes in layers creating a rhombohedral structure. Gray in shape: it is characterized by its metallic shape.Considered the structural unit of yellow antimony. Yellow: where it is a stable metal and composed of Sb4 molecules.Also, it is used in various alloys, such as the bearing metal obtained by being alloyed with tin, tin and the English metal product of the alloy with zinc. This semi-metal is widely used as an alloy, it greatly increases the strength and mechanical hardness of lead. On the other hand, antimony characterized by its high purity is obtained by electrolytic refining. In the same way it is used in the formation of certain alloys with metals, as is the case of lead, where when mixed with this element it becomes harder, being used in the manufacture of batteries, weapons, ammunition, cable coverings, cushions, bearings and other industrial products.Īntimony is obtained by heating sulfide and iron, or by heating sulfide with the sublimate of Sb4O6 and reducing it with carbon. It is widely used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, diodes and infrared detectors in its pure form. If exposure is prolonged, it can cause diarrhea, heart problems, lung disease, ulcers, severe vomiting, etc. It usually occurs naturally in the environment, when people are exposed to it in high doses it can cause effects on their body such as irritation of the lungs, eyes and skin.It is stable in air at normal temperatures, but when heated it will burn creating glow and white Sb2O3 smoke.It has four allotropic forms: black and yellow antimony, which are stable, non-metallic forms, white, which has a bluish-white tint, and its crystalline solid form, which is its most basic form.It is distinguished by its bluish white color with metallic reflections and a scaly appearance. Metallic antimony can be broken easily.It is found in nature as Sb2S3 (stibine, antimonite).It has excellent electrical conductivity.Coming to present intermediate properties between non-metals and metals. It belongs to the group of metalloids or semi-metals.In its natural form, it comes in a solid state.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
